Nesting index entries
The technique of nesting indexterm elements can produce multi-level indexes in output documents.
You can created multi-level (secondary and tertiary) indexes by nesting indexterm elements.
<indexterm>EJ25 engine
<indexterm>performance</indexterm>
</indexterm>EJ25 engine
performance .................... 15
The page reference is applied to the innermost term (in the example,
performance
) only.
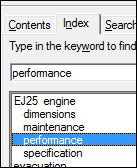
EJ25 engine
dimensions .................... 72
maintenance .................... 33
performance .................... 15
specifications .................... 49
You should avoid nesting index entries to more than three levels. In most cases, one or two levels will provide sufficient scope for a comprehensive and easy-to-navigate index.
If you have a number of secondary entries belonging to the same parent
entry, such as
EJ25 engine, performance
and
EJ25 engine, torque
, the secondary entries can either be nested
under the same parent entry, or structured separately.
<indexterm>EJ25 engine
<indexterm>performance</indexterm>
<indexterm>torque</indexterm>
</indexterm><indexterm>EJ25 engine
<indexterm>performance</indexterm>
</indexterm>
<indexterm>EJ25 engine
<indexterm>torque</indexterm>
</indexterm>